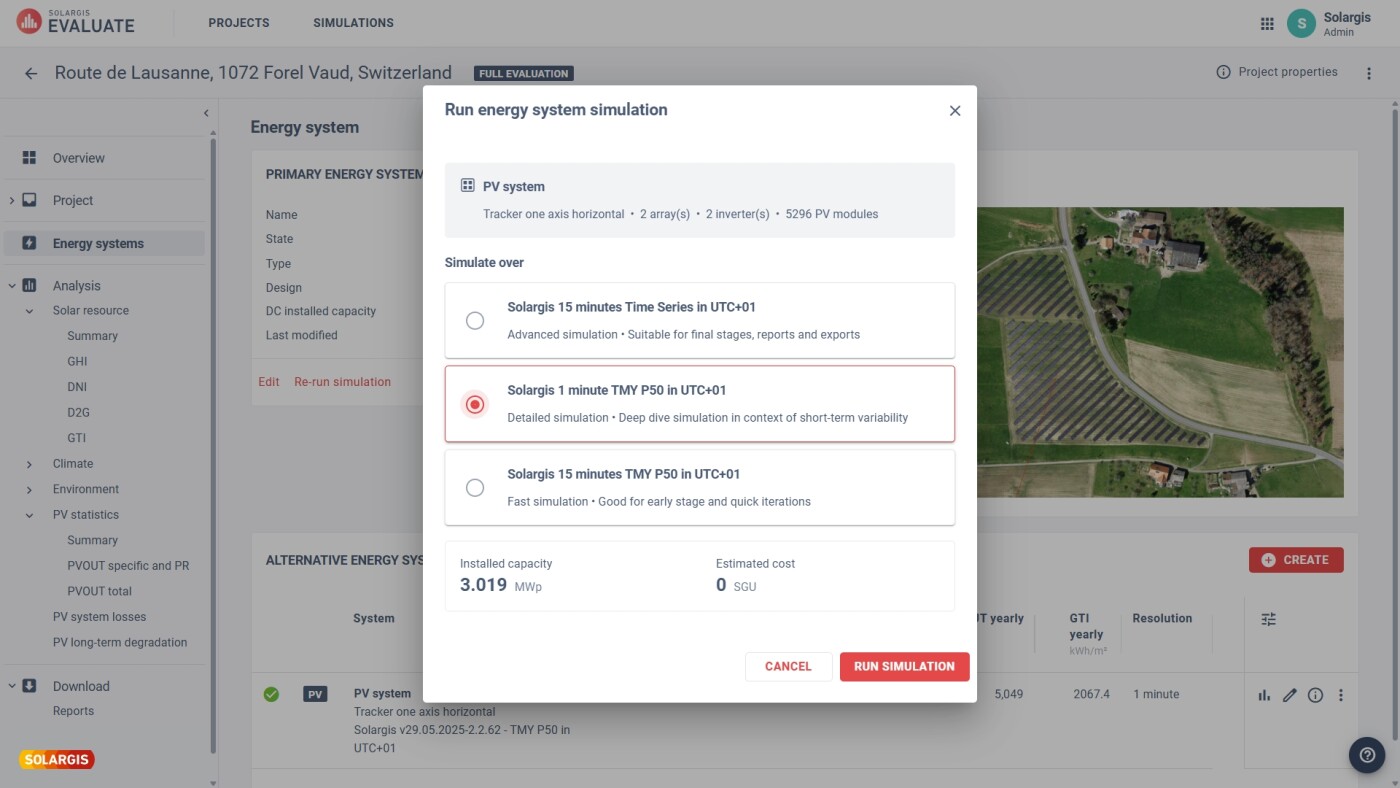
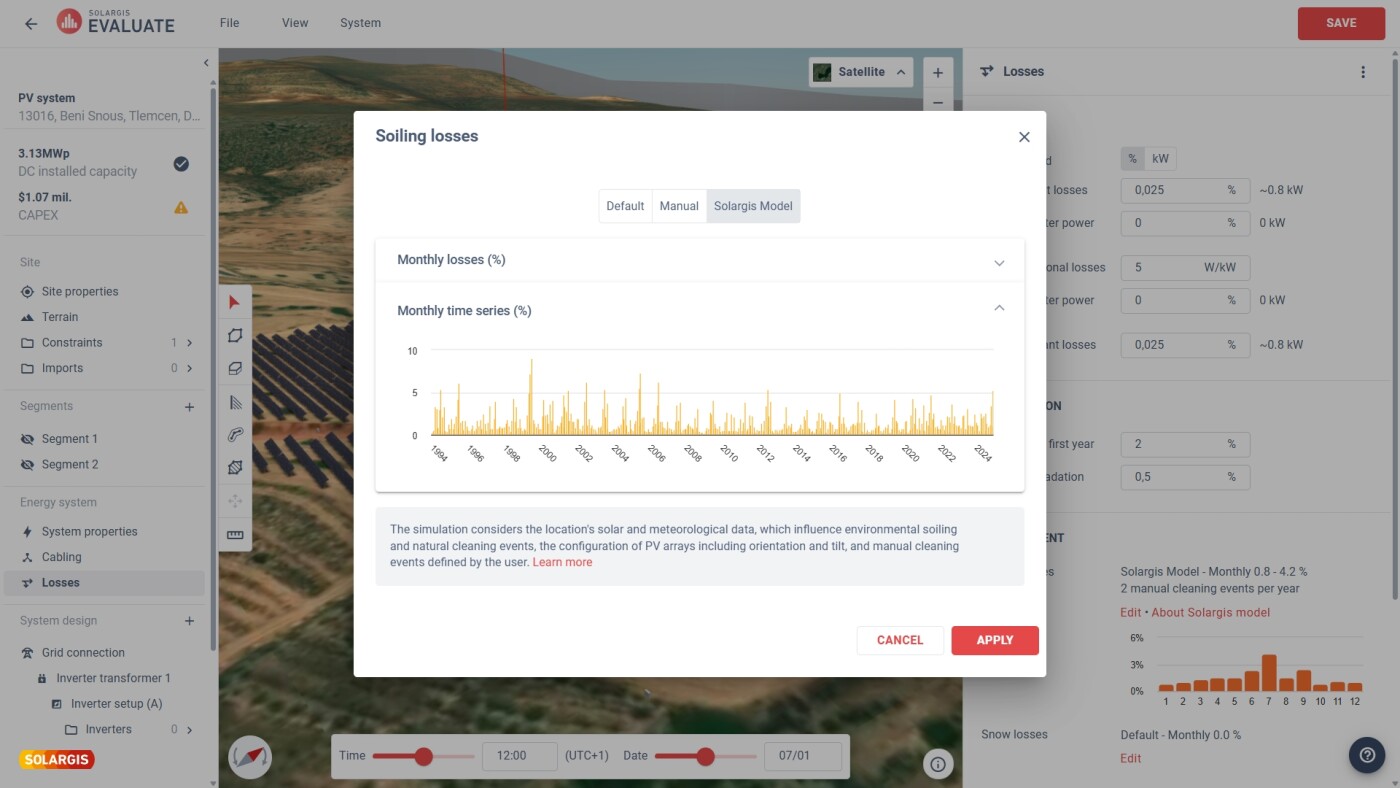
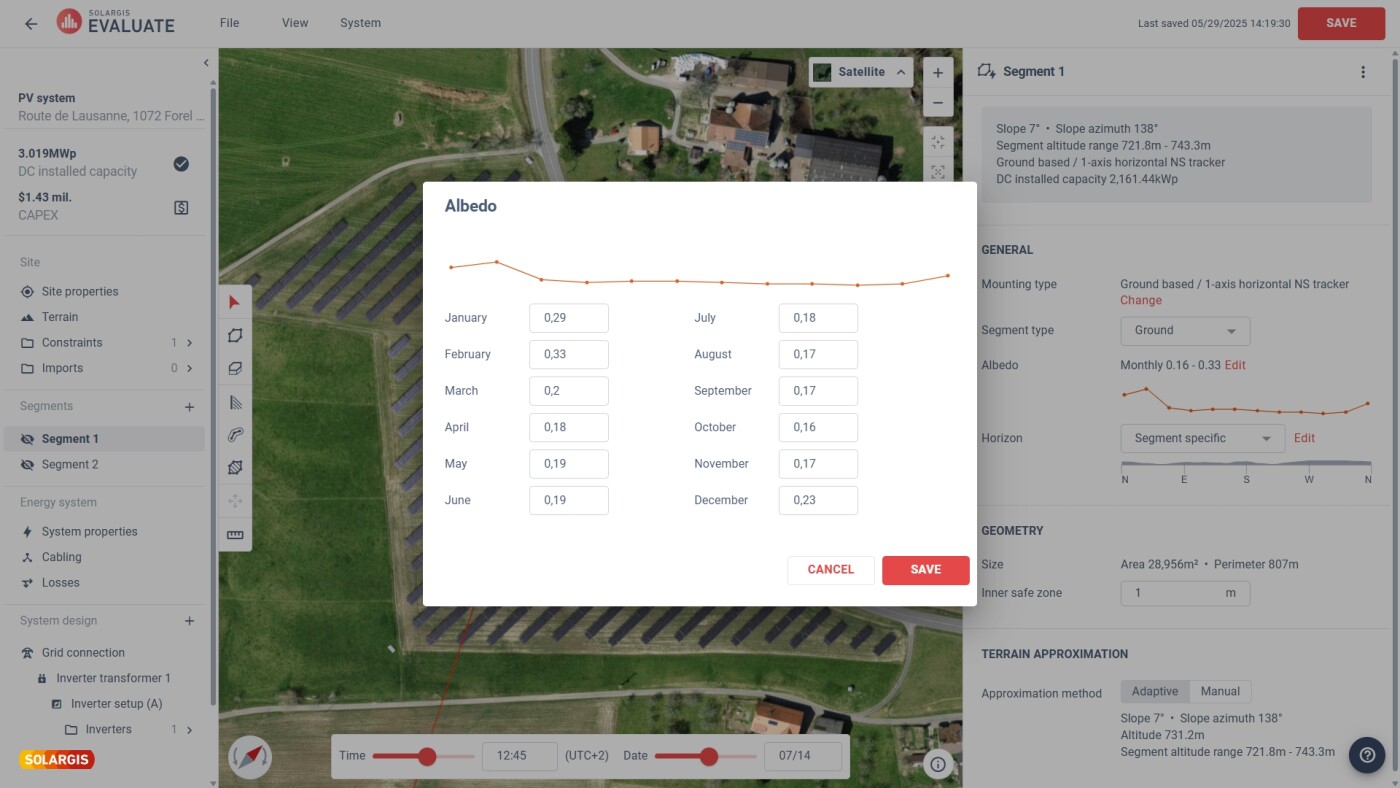
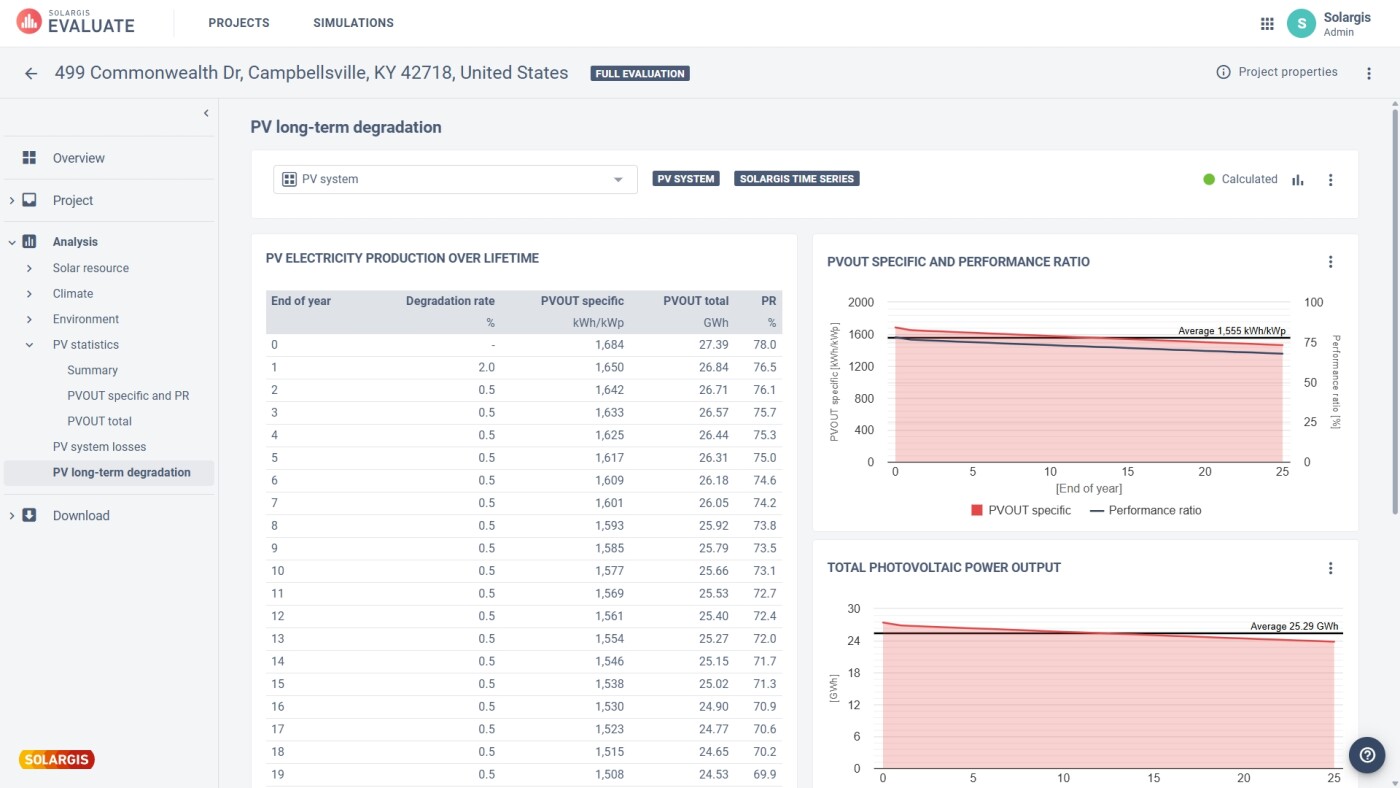
When designing a PV power plant, it is possible to choose from multiple terrain models that lead to different layouts:
-
Copernicus in 30m resolution (1 arcsec | global | 2011-2015 | surface model - including trees and buildings)
-
SRTM (Google Earth) in 30m resolution (1 arcsec | global | 2000 | terrain model - excluding trees and buildings)
-
SRTM (Solargis) in 90m resolution (3 arcsec | global | 2000 - 2017 | terrain model - excluding trees and buildings)
- Upload your own terrain elevation data in GeoTIFF format if you want to override the terrain model with higher-resolution or project-specific data
To support more effective site planning, you can highlight areas that exceed a specified slope threshold, making it easier to identify zones that may require fixed-mount structures or more precise tracker placement.
Experimenting with different elevation data results in different energy yields, but doesn’t affect solar and meteorological data. Horizon shading is calculated from the environmental data and depicts the terrain elevation and shading in the location’s surroundings. You can modify and enter your own horizon data if needed.
More about the importance of terrain data ->