本页未翻译。您正在浏览的是英文版本。
We’re introducing eight new map layers in Solargis Prospect, designed to provide quick insights into factors affecting the performance, durability, and risk profile of photovoltaic (PV) systems.
These new layers offer essential data for PV project engineers, developers, and financial planners, helping them make informed decisions about site selection, system design, and long-term investment strategies.
The latest update brings eight new map layers to the Solargis Prospect platform:
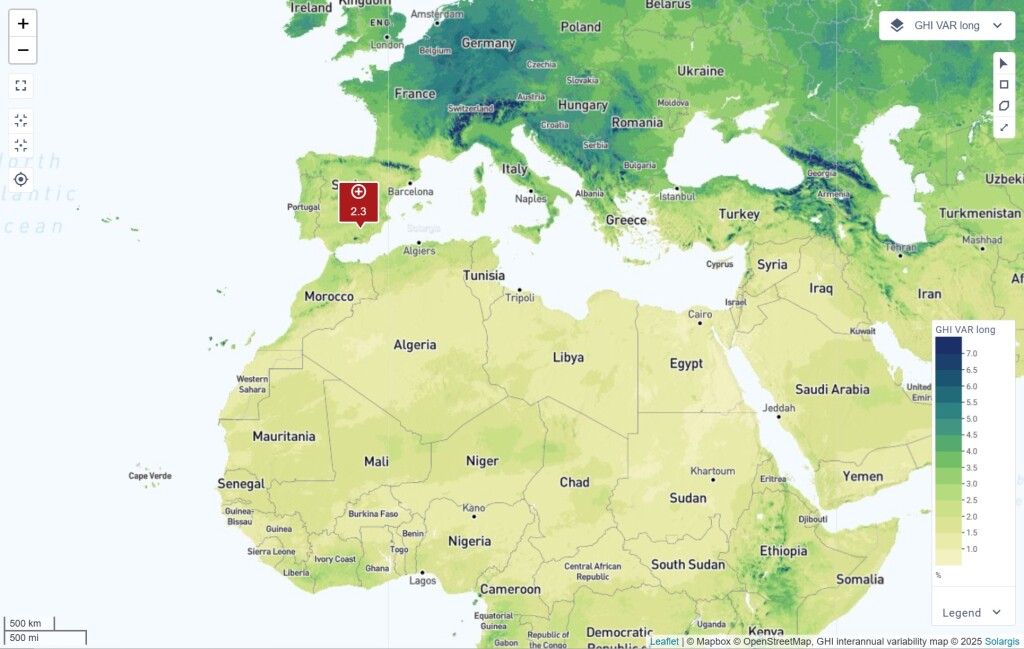
Solargis Prospect now includes a global map and data detailing interannual solar resource variability, helping you assess year-over-year fluctuations in solar irradiation. By understanding these long-term trends, you can evaluate financial risks and planning stability and compare solar resource stability across different locations or regions.
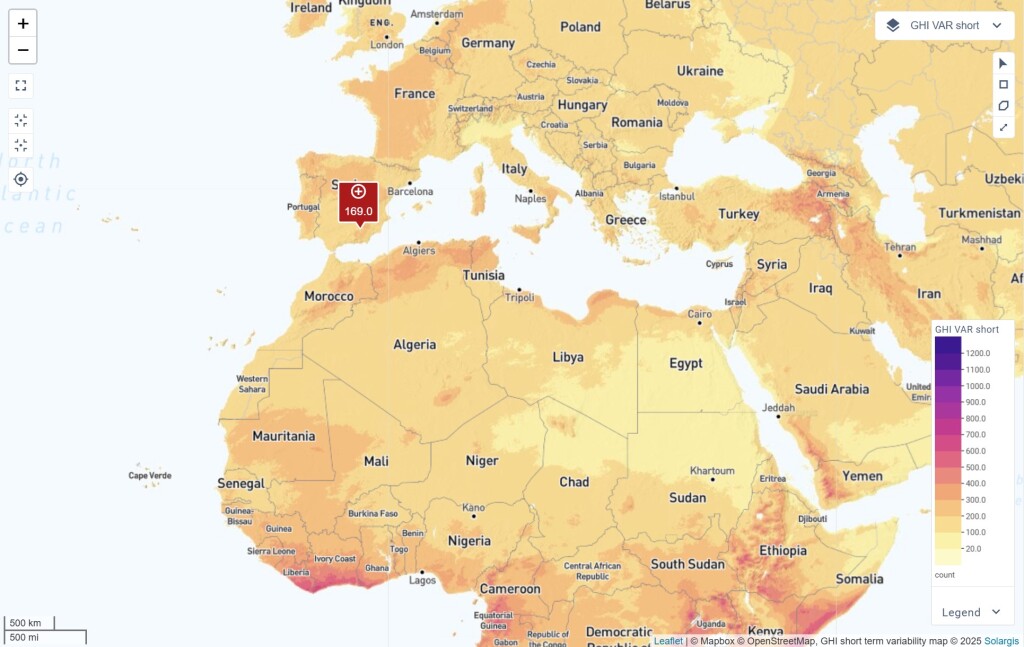
Solar resource intermittency—caused by forming and moving clouds—is a challenge for PV plant operations and grid balancing. This map layer shows daily fluctuations in solar irradiation, enabling better system design, energy storage planning, and grid integration.
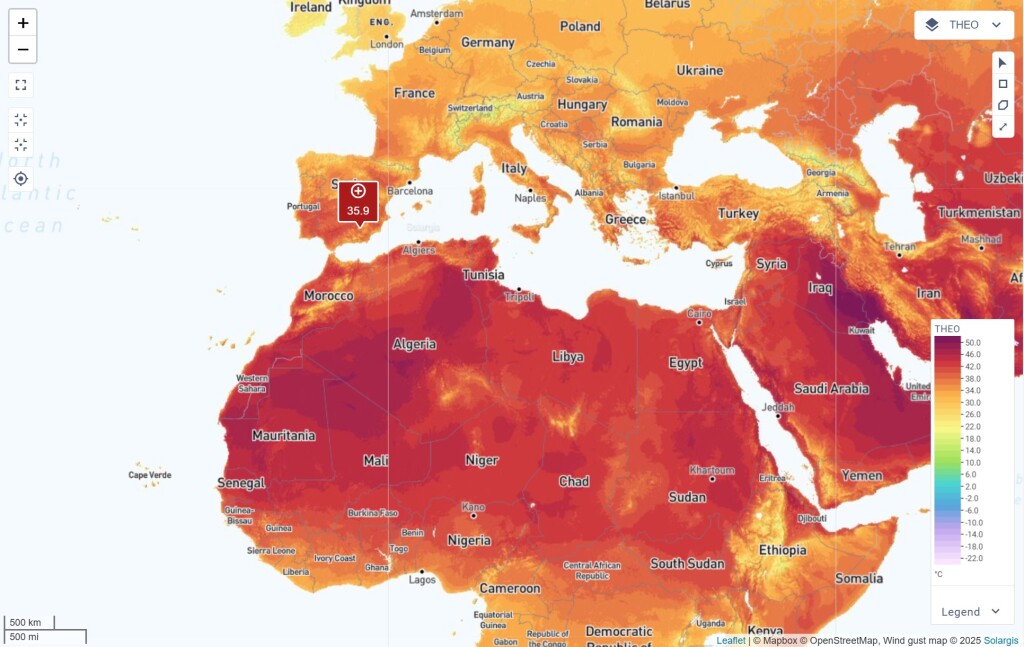
Extreme heat negatively impacts PV efficiency, lifespan, and reliability of PV systems. This map layer helps assess temperature tolerance limits, allowing you to identify potential risks and implement appropriate mitigation measures to protect PV systems.
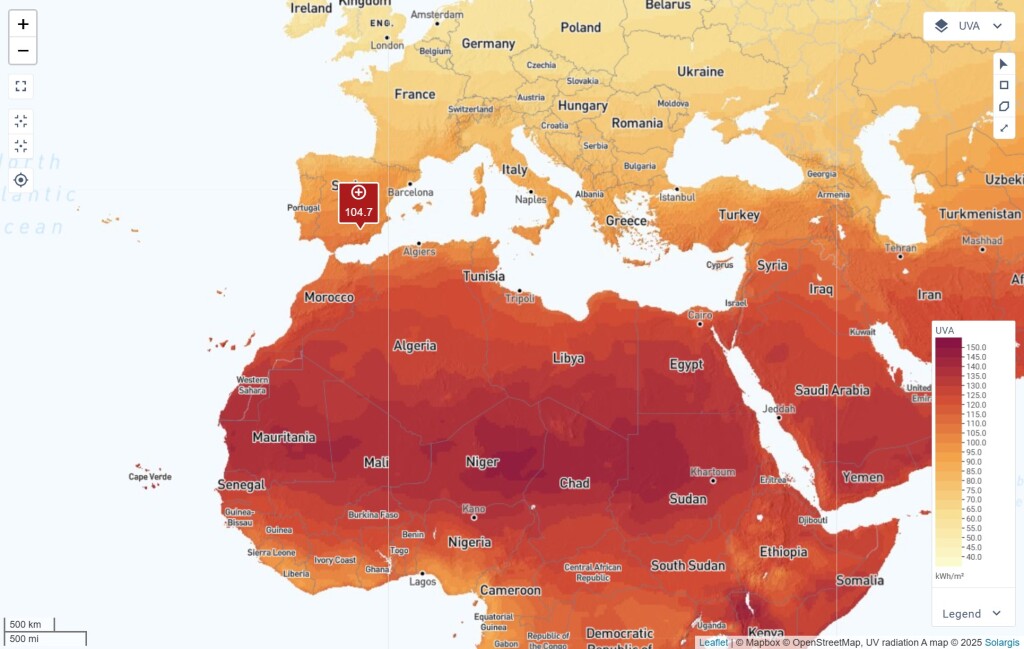
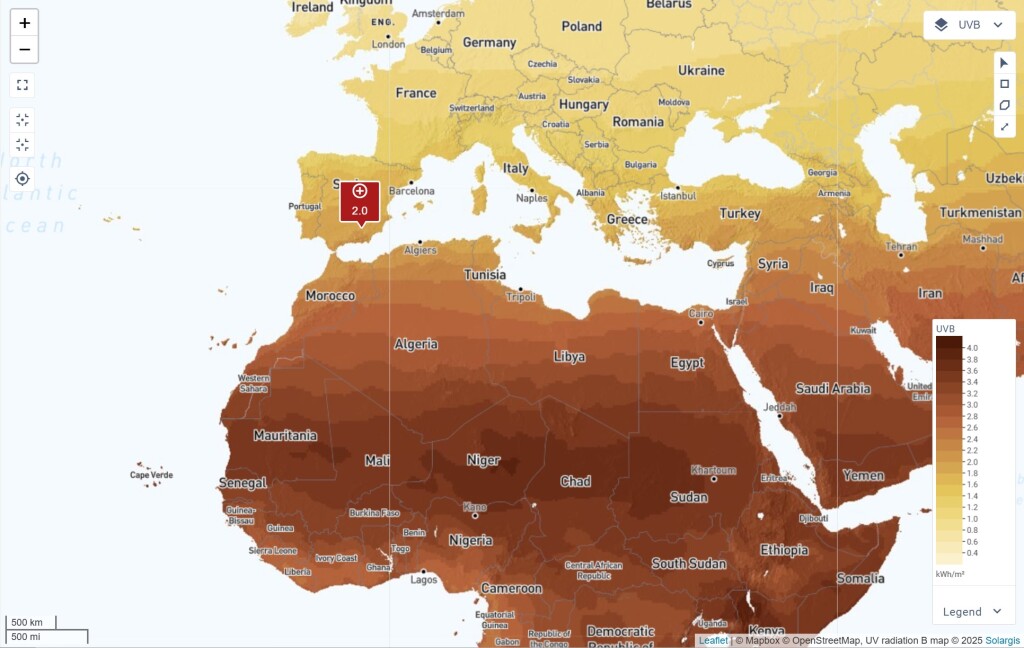
UV radiation accelerates material degradation, causing cracking, discoloration, and reduced performance in PV modules. The UVA and UVB maps allow users to compare UV exposure across different locations, assess failure risks, and select components with higher UV resistance for improved durability.
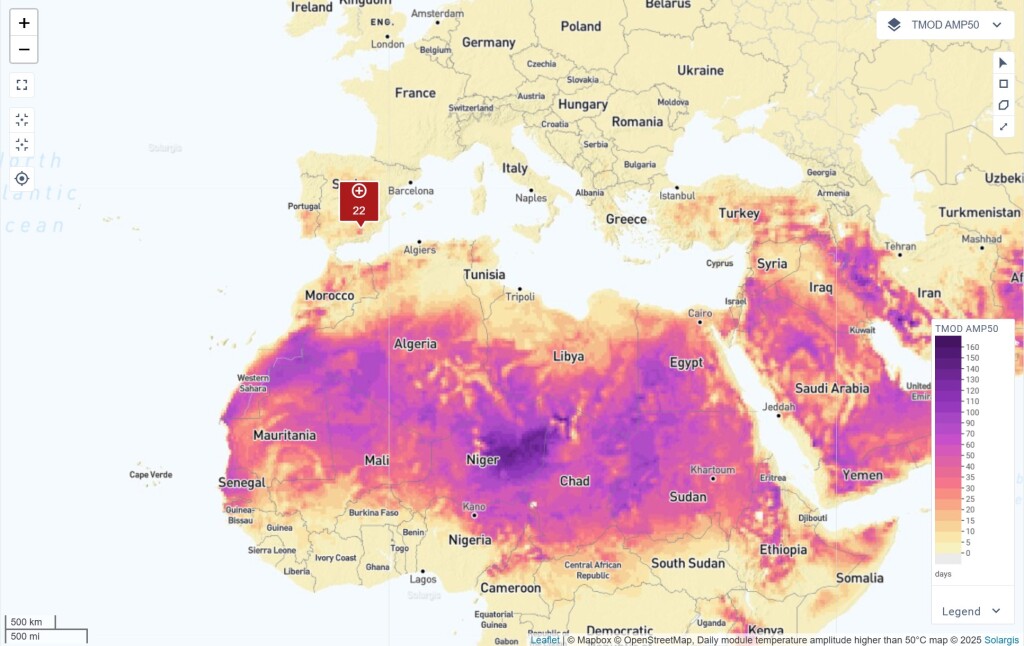
Thermal cycling is a major cause of PV module degradation. This map helps users assess the frequency of extreme temperature fluctuations at a project site, enabling better risk assessment and mitigation planning. It also facilitates regional comparisons to optimize PV system placement.
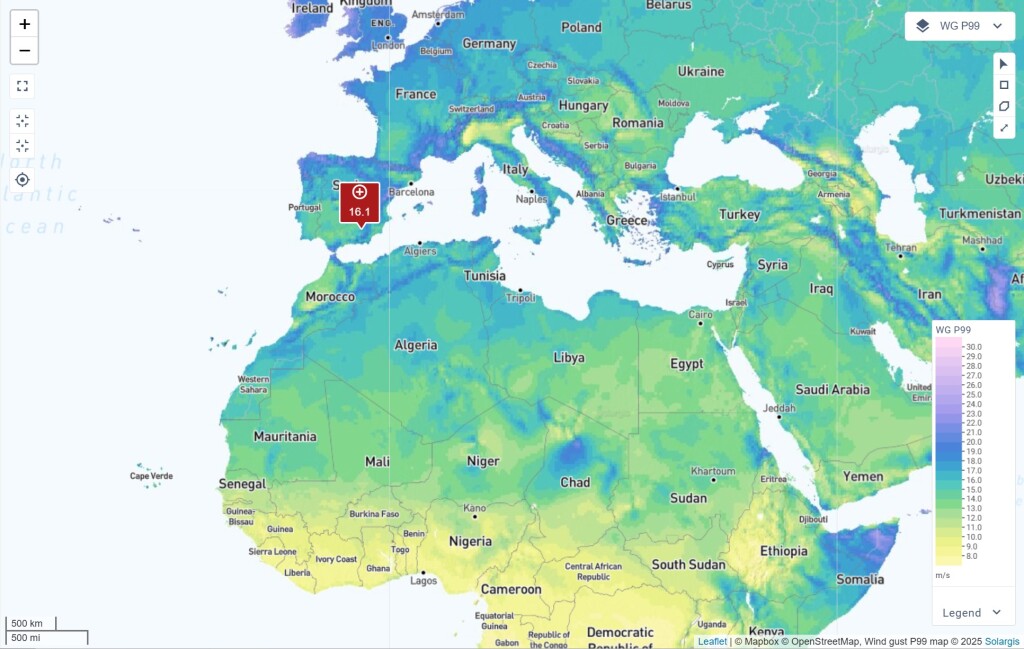
Wind gusts affect PV module stability, tracking systems, and overall energy output. This layer provides data on extreme wind conditions, helping optimize module design, tracker selection, and structural safety to reduce energy losses and prevent damage.
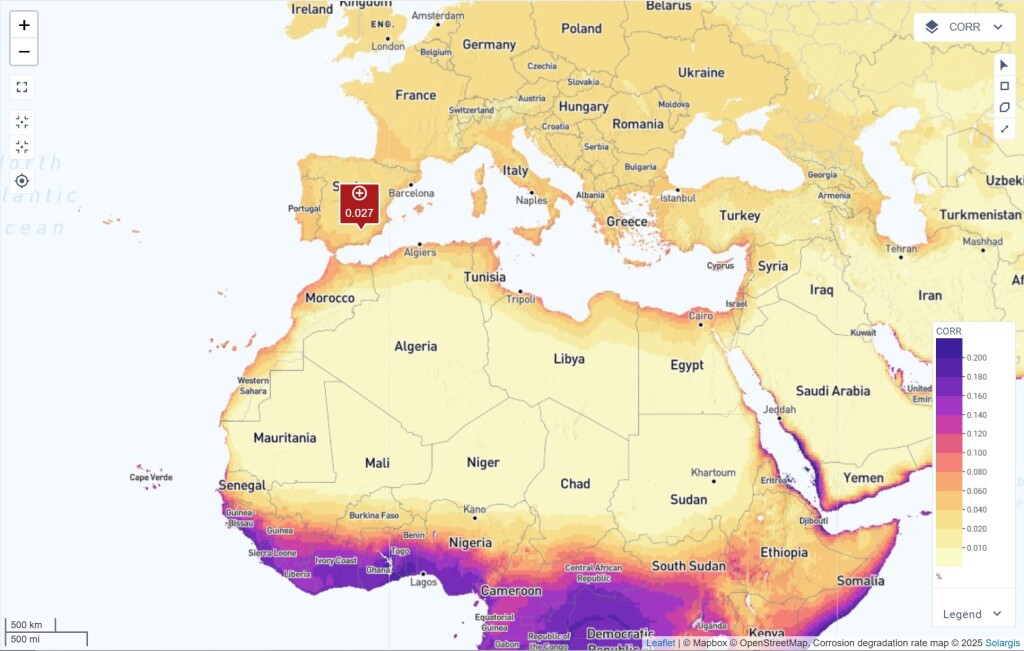
High temperatures and humidity accelerate corrosion, impacting PV module performance and longevity. It also weakens the electrical connections, increases leakage currents, and reduces power output over time. This map layer helps users assess corrosion risks in different environments, aiding in module selection, maintenance planning, and project siting.
Find more details about the new map layers in Solargis Knowledge Base.